People often ask, “Should I invest in a traditional or Roth IRA when planning for retirement? What’s the difference?” To answer this question, let’s discuss the basics.
Traditional vs. Roth
An IRA is an individual retirement account that is not associated with your employer. When opening an IRA, you will have to choose either traditional or Roth. This is not to say that you are limited to one account for your lifespan. Depending on your income and the stage of your career, both types can be beneficial.
Generally, Roth IRAs are best suited for younger individuals because they have a long working life before they retire, and that large time-frame gives their investments time to increase substantially. This increase will not be taxable when drawn out during retirement. Roth IRAs also come with an income limit, so it is ideal for those at entry-level or mid-level in their careers.
Traditional IRAs are best suited to those who are in a higher tax bracket. These individuals will save significant tax dollars immediately through tax-deductible contributions and will likely be in a lower tax bracket when they retire because their income will be reduced. This usually describes mature individuals who are in their later years of working and usually have higher incomes. Therefore, the tax savings now are greater, and the time for investments to increase in value is shorter.
Withdrawing Your Savings
When you decide to put money in a retirement account, it is ideal to leave that investment untouched until you are retired. Traditional IRAs have stricter rules about early withdrawals than Roth accounts. The penalty for early withdrawal (before age 59.5) from a Traditional IRA is 10%, and you pay income tax on the amount you withdraw. Roth IRA withdrawals are tax and penalty free if you withdraw upon reaching age 59.5 and the account has been established for five or more years.
Traditional IRAs impose Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) when you turn 72; this is a minimum amount that you must withdraw each year from your account. These withdrawals are considered taxable income. To find your RMD, use this worksheet from the IRS.
Roth IRAs do not impose RMDs, and the withdrawals are not considered taxable income.
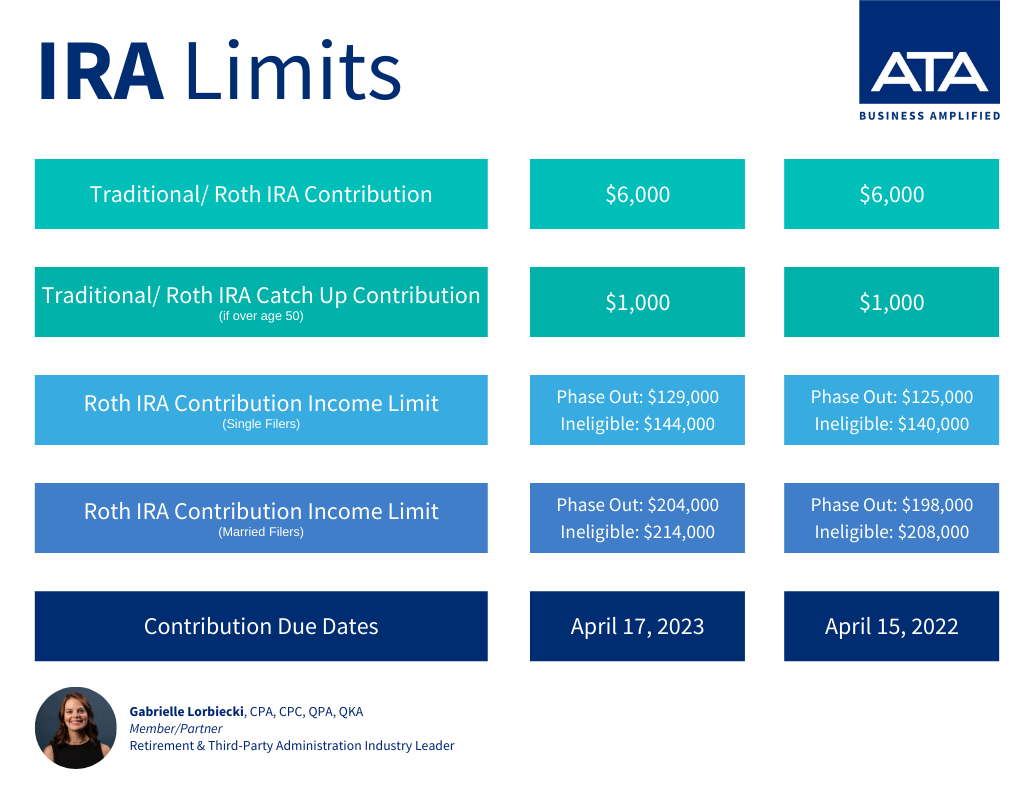
Both Traditional and Roth IRAs have contribution limits and due dates that vary year-to-year. You can find those amounts and dates in the graphic below.
For more information and consultation about IRAs and retirement planning, contact industry leader Gabrielle Lorbiecki or visit https://ata.net/ata-retirement.